-
Order Online Now ! +8615950652197
-
Call Us Now ! admin@zkmetalpipe.com
TIG (tungsten inert gas) welding and MIG (metal inert gas) welding are two common methods of welding used to join metal components.
MIG Process
Metal insert gas (MIG) welding uses a semi-automatic or fully automatic arc to create the weld with a consumable wire electrode as the filler material and a shielding that is usually a mix of 75% argon and 25% CO2 gas to protect the weld, promote weld penetration and reduce weld bead porosity.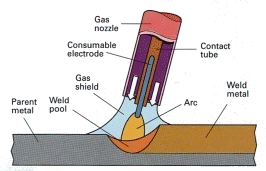
TIG Process
Tungsten inert gas (TIG) welding is also called gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW). As with MIG, this welding process also uses an arc but, unlike with MIG, the electrode is a non-consumable tungsten electrode that is used alongside a separate consumable filler material. This filler is usually a rod that is manually fed into the weld pool, meaning that both hands are used for TIG welding – one for the tungsten electrode and the other for the filler rod.
The composition and size of the filler rod varies according to the weld being made. TIG welding also uses a shielding gas, although this is typically 100% argon as CO2, as used with MIG, promotes tungsten oxide formation that can prematurely wear your electrode and contaminate the weld.
MIG Advantages and Disadvantages
MIG welding tends to be used to join large and thick materials, using a consumable wire that is both the electrode and filler material.MIG welding is faster than TIG welding, creating shorter production times for welds and, subsequently, lower costs. MIG welding is also easier to learn, making it easier to produce welds that require little or no cleaning and finishing.However, MIG welds are not as precise, strong or aesthetically pleasing as those produced by a skilled TIG welder.
TIG Advantages and Disadvantages
TIG welding is a versatile technique that is capable of joining a wide range of small and thin materials, using a non-consumable tungsten electrode alongside an optional, separate filler rod.TIG welding is slower than MIG welding, which increases production times and, subsequently, leads to increased costs. TIG welding is also harder to learn and requires skilled practitioners to deliver the correct weld precision and accuracy.However, because TIG provides greater control over the welding operation, TIG welds are stronger, more precise, and more aesthetically pleasing than MIG welds.
MIG Applications
Because MIG welding is easy to learn, relatively simple to perform and able to join materials such as aluminium, mild steel and stainless steel, it is suitable for a range of applications.MIG is particularly effective for thicker metals and typically used where weld aesthetics are not a priority.
TIG Applications
TIG welding is more difficult to learn, but offers more precise results than MIG welding. TIG is also better for joining thinner materials and can be used to weld aluminium, copper, steel, titanium and more.As such, TIG welding is widely used jobs where precision is required, such as for aerospace, motorsport, industrial structures, production line manufacture, and more.